Some possible standards for the 4G system are 802.20, WiMAX (802.16), HSDPA, TDD UMTS, UMTS and future versions of UMTS and proprietary networks from ArrayComm Inc., Navini Networks, Flarion Technologies, and 4G efforts in India, China and Japan.
The design is that 4G will be based on OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing), which is the key enabler of 4G technology. Other technological aspects of 4G are adaptive processing and smart antennas, both of which will be used in 3G networks and enhance rates when used in with OFDM.
Currently 3G networks still send there data digitally over a single channel, OFDM is designed to send data over hundreds of parallel streams, thus increasing the amount of information that can be sent at a time over traditional CDMA networks.
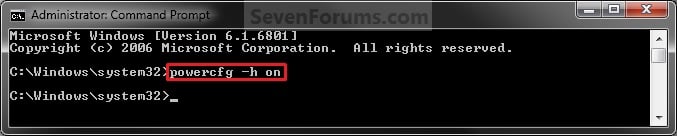
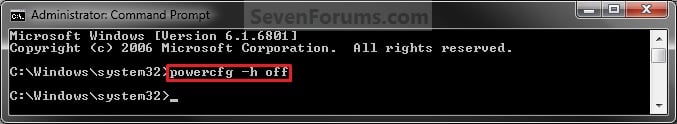
The 4G data rates will vary depending on the number of channels that are available, and can be used. The channels that can be used will be cleaner thanks to technologies like adaptive processing, which detects interference on a channel and improves reception by actively switching channels to avoid interference.
4G networks will also use smart antenna technology, which is used to aim the radio signal in the direction of the receiver in the terminal from the base station. When teamed up with adaptive techniques, multiple antennas can cancel out more interference while enhancing the signal.
The 4G plans are still years away, but transitioning from 3G to 4G should be seamless for customers because 4G will have evolved from 3G. Users won't even have to get new phones. Digital applications are getting more common lately and are creating an increasing demand for broadband communication systems. The technical requirements for related products are very high but solutions must be cheap to implement since we are essentially talking about consumer products. For Satellite and for Cable; such cost-efficient solutions are already about for the terrestrial link (i.e. original TV broadcasting) the requirements are so high that the 'standard' solutions are no longer an option. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a technology that allows transmitting very high data rates over channels at a comparable low complexity. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing is the choice of the transmission method for the European digital radio (DAB) and Digital TV (DVB-T) standard. Owing to its great benefit’s OFDM is being considered for future broadband application such as wireless ATM as well.
First of all the FDM part - Frequency division multiplexing is a technology that transmits several signals at the same time over a single transmission path, in a medium such as a cable or wireless system. Each signal is transmitted inside its own unique frequency range (the carrier frequency), which is then modulated by the data that is needing to be transmitted.
Orthogonal FDM's spread spectrum technique spreads the data over a lot of carriers that are spaced apart at precise frequencies. This spacing provides the "orthogonality" in this method which prevents the receivers/demodulators from seeing frequencies other than their own specific one. The main benefit of OFDM is high spectral efficiency, but with OFDM you also get; high resiliency to RF interference, and the multi-path distortion is lower. This is handy because in a standard terrestrial broadcasting situation there are high amounts of multipath-channels (e.g. the signal that was sent arrives at the receiving end using multiple paths of different lengths). Since the various versions of the signal interfere with each other, known as inter symbol interference (ISI) it becomes incredibly hard to extract the original information.